The North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) at NC State University is celebrating its 35th anniversary in 2023. The NCCETC has dedicated more than three decades to advancing a sustainable energy economy by educating, demonstrating and providing support for clean energy technologies, practices, and policies.
The North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) at NC State University is celebrating its 35th anniversary in 2023. The NCCETC has dedicated more than three decades to advancing a sustainable energy economy by educating, demonstrating and providing support for clean energy technologies, practices, and policies.
Founded in December 1987 as the North Carolina Solar Center, NCCETC was first established through a partnership among the state government of North Carolina, NC State University, and the solar industry with sponsorship from the Energy Division of the NC Department of Commerce (now known as the State Energy Office). The North Carolina Solar Center was created to meet the need for a central clearinghouse that could assist the state’s citizens, businesses, and institutions in using solar energy.
Over the years, NCCETC’s focus expanded into a broader array of renewable energy resources, alternative transportation technologies, clean power technologies and industrial energy efficiency. In 2003, environmental leaders from across North Carolina gathered to dedicate an Alternative Fuels Vehicle (AFV) Demonstration Facility while celebrating the 15th anniversary of NCCETC. The AFV Facility served as a research and education facility for a variety of alternative fuels, adding clean transportation to NCCETC’s outreach, education and research activities.
Clean transportation is one of the primary programmatic areas of focus for NCCETC today. Working with government, non-profit organizations and businesses, NCCETC is helping diversify fuel supplies and support clean, more vibrant local and state economies with the ultimate goal of cleaner air and greater energy diversity.
 Anne Tazewell joined NCCETC in July 2004 and shortly thereafter established the Clean Transportation program before successfully obtaining funding for the Clean Fuel Advanced Technology (CFAT) project. Tazewell remained at NCCETC for 17 years before she retired in 2021. “I quickly fell in love with the idea of public service and working with others to serve the greater good,” said Tazewell.
Anne Tazewell joined NCCETC in July 2004 and shortly thereafter established the Clean Transportation program before successfully obtaining funding for the Clean Fuel Advanced Technology (CFAT) project. Tazewell remained at NCCETC for 17 years before she retired in 2021. “I quickly fell in love with the idea of public service and working with others to serve the greater good,” said Tazewell.
To move forward this mission, Tazewell secured regional Congestion Mitigation Air Quality (CMAQ) funding to open the state’s first publicly accessible biodiesel service station in Garner, NC. In 2006 and 2009, NCCETC was awarded a total of $2.6 million in CMAQ funding from the NC Department of Transportation and Federal Highway Administration to reduce transportation related emissions in North Carolina counties that do not meet national air quality standards.
The NC Division of Air Quality and State Energy Office also contributed $200,000 each to support the CFAT project. The three million dollar project encompasses three broad areas: education and outreach, recognition of exemplary activities, and direct project funding. From 2006 through 2019, NCCETC has provided $11.9 million in federal funds to help private and public fleets in North Carolina purchase clean transportation technologies to improve the state’s air quality.
In 2020, Tazewell efforts were recognized with the Lifetime Achievement Award by the NC Sustainable Energy Association for being a tireless champion of clean air and clean energy. Tazewell explained she first entered into clean energy to express her passion for reducing oil dependence. Before joining NCCETC, she worked at the Triangle J Council of Governments where she saw the power of public and private partnerships for advancing affordable domestic transportation fuels, energy efficient mobility systems, and other fuel-saving technologies.
One key project completed during Tazewell’s tenure was the tracking and compliance on behalf of the state of the Petroleum Displacement Plan (PDP) Provision, mandated by the NC General Assembly. Implementation of the PDP requirement in fiscal year 2010-2011 has resulted in a 16% reduction in petroleum use by state fleet vehicles as compared to the baseline of fuel use established in fiscal year 2004-2005, through the use of alternative fuels, efficient vehicles and other policies and practices that conserve fuel.
Providing Technical Assistance & Fleet Education
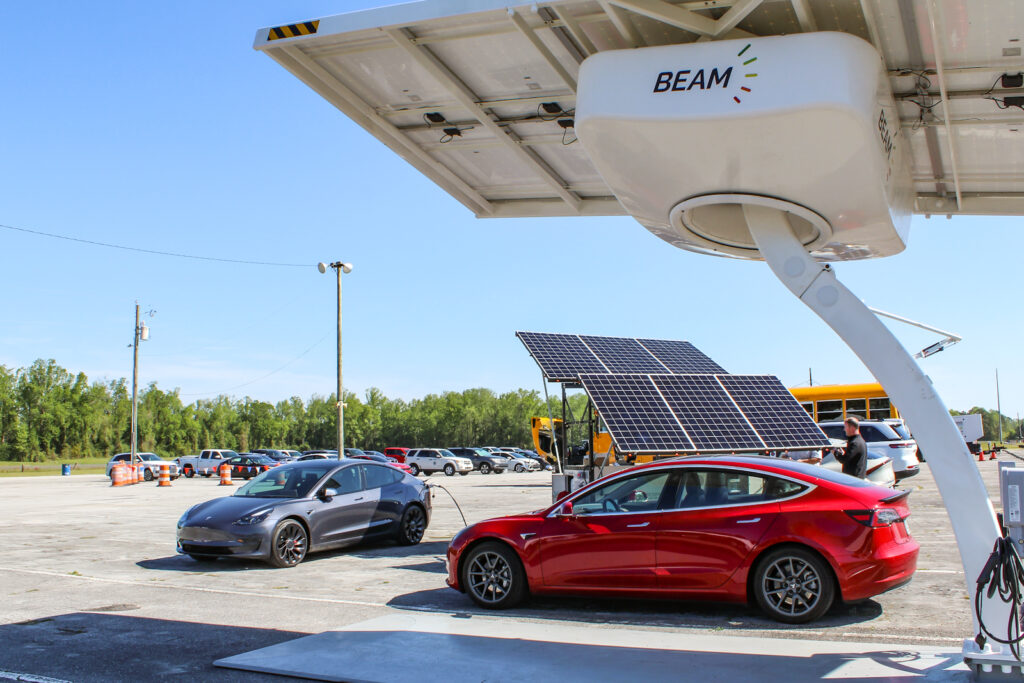
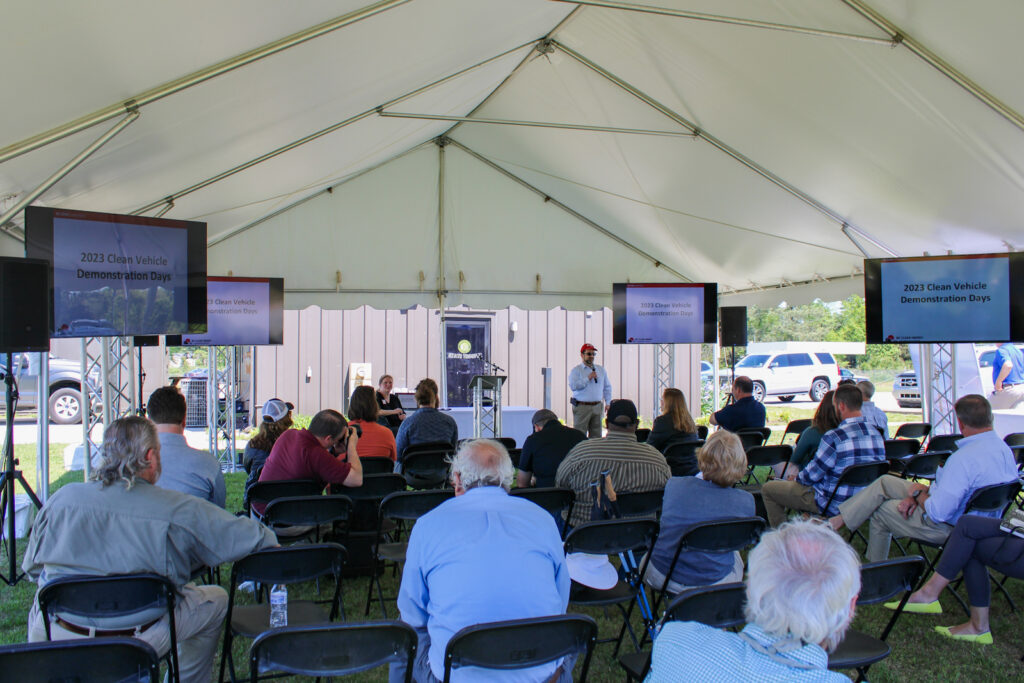
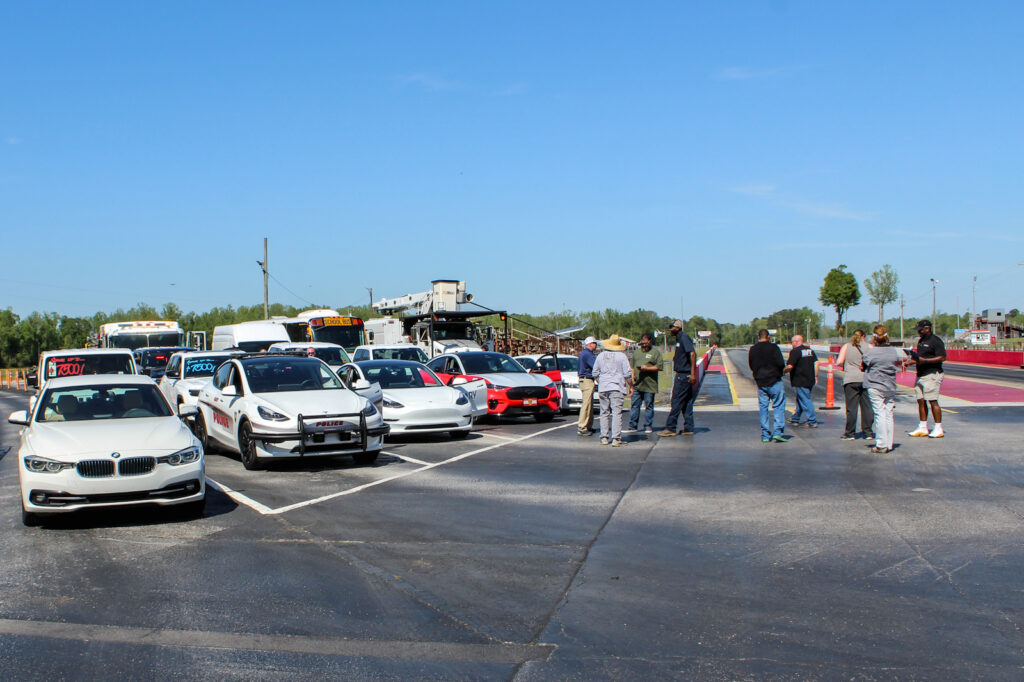
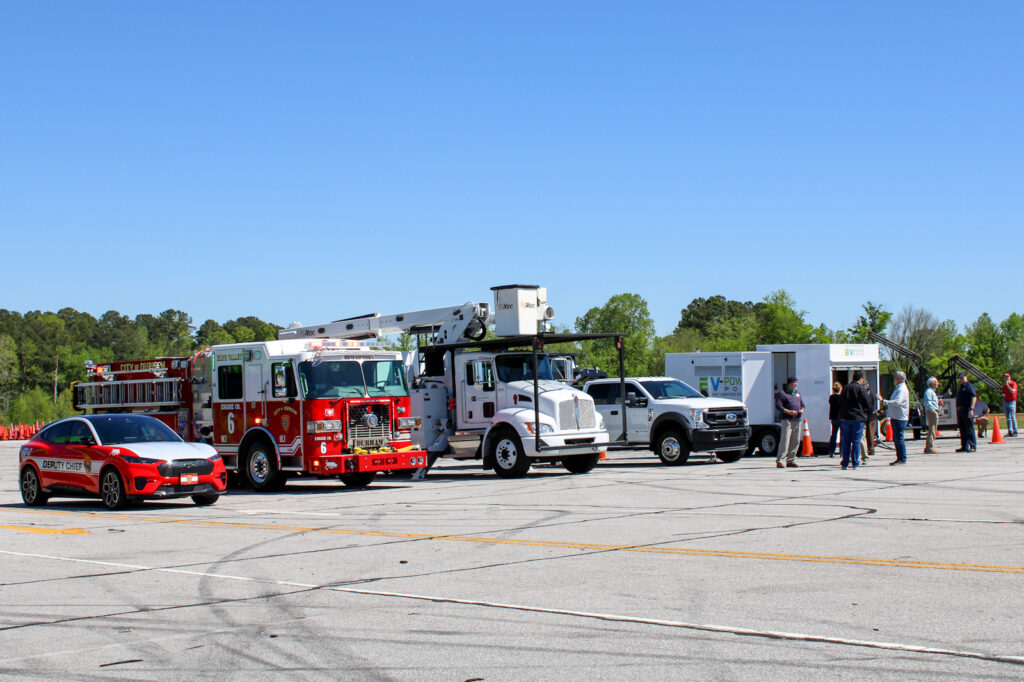
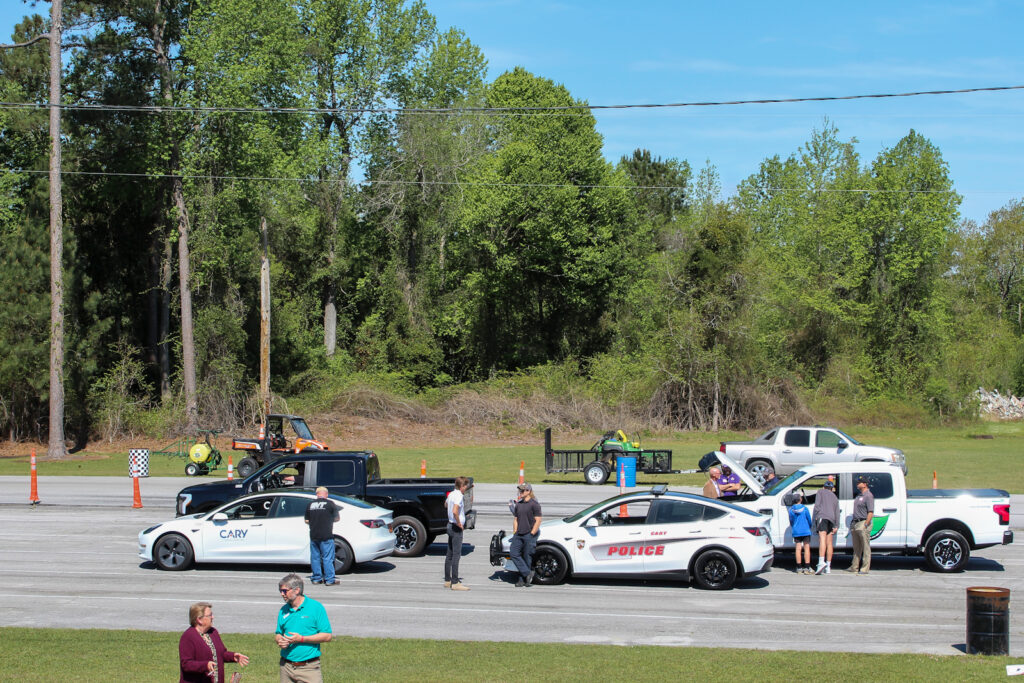
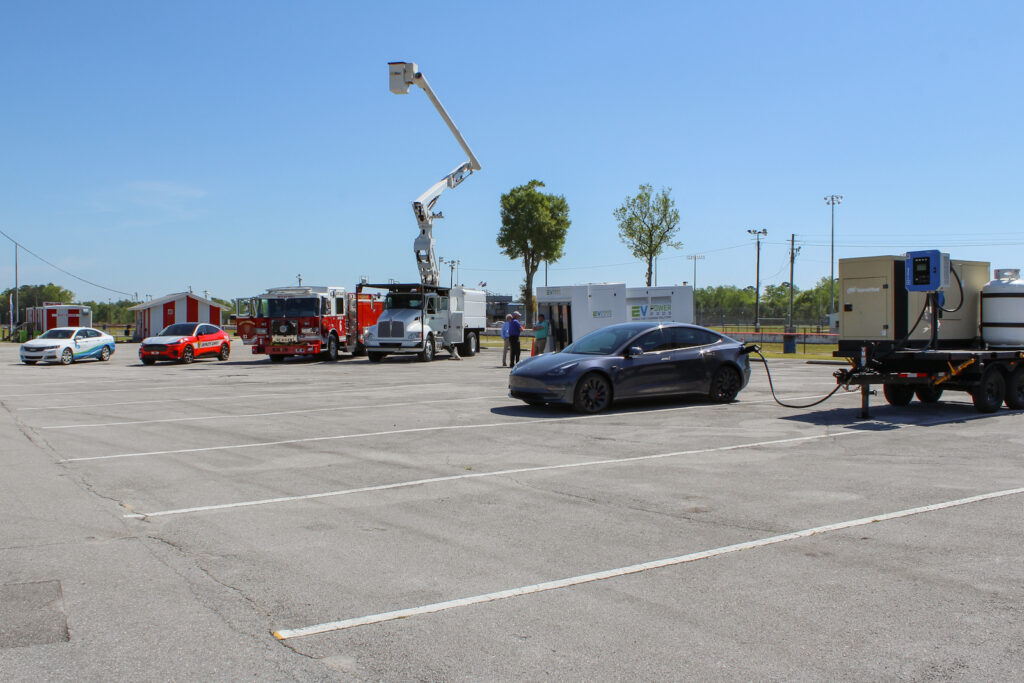
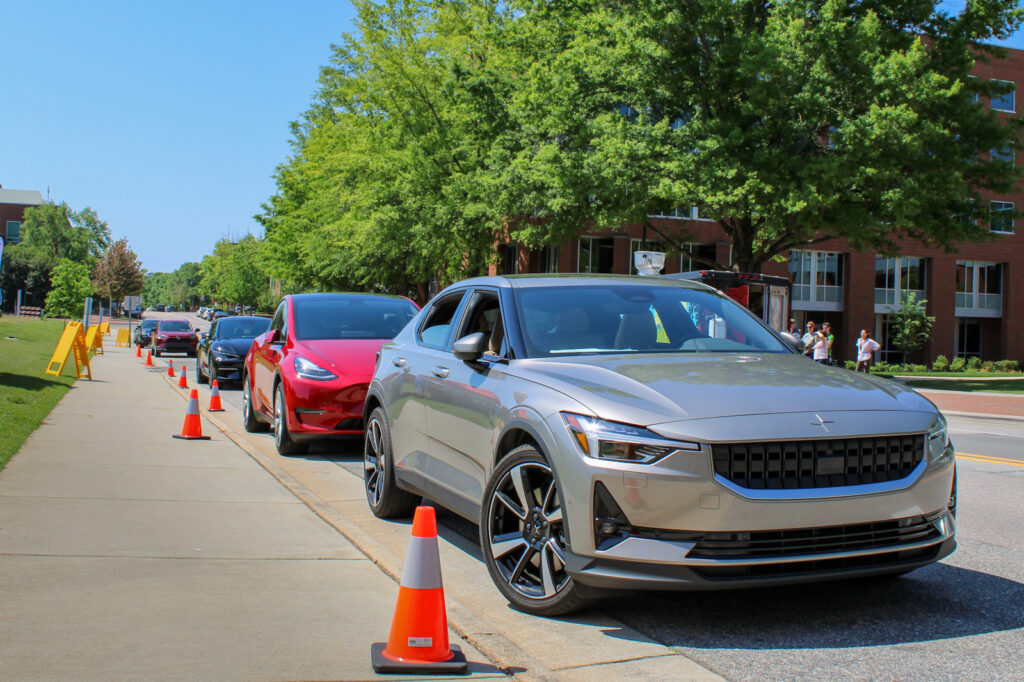
 NCCETC engages with government entities and employees through a variety of ways including holding Clean Transportation Demonstration Days where attendees come from across North Carolina to gain education and experience with clean transportation technologies. The Clean Transportation team hosted two Clean Transportation Demonstration Days this year in April – one in Garner and one in Jacksonville, North Carolina – where hundreds of attendees were able to hear about real-world case study results, experience hands-on static review of technologies, network and participate in a closed-course ride and drive.
NCCETC engages with government entities and employees through a variety of ways including holding Clean Transportation Demonstration Days where attendees come from across North Carolina to gain education and experience with clean transportation technologies. The Clean Transportation team hosted two Clean Transportation Demonstration Days this year in April – one in Garner and one in Jacksonville, North Carolina – where hundreds of attendees were able to hear about real-world case study results, experience hands-on static review of technologies, network and participate in a closed-course ride and drive.
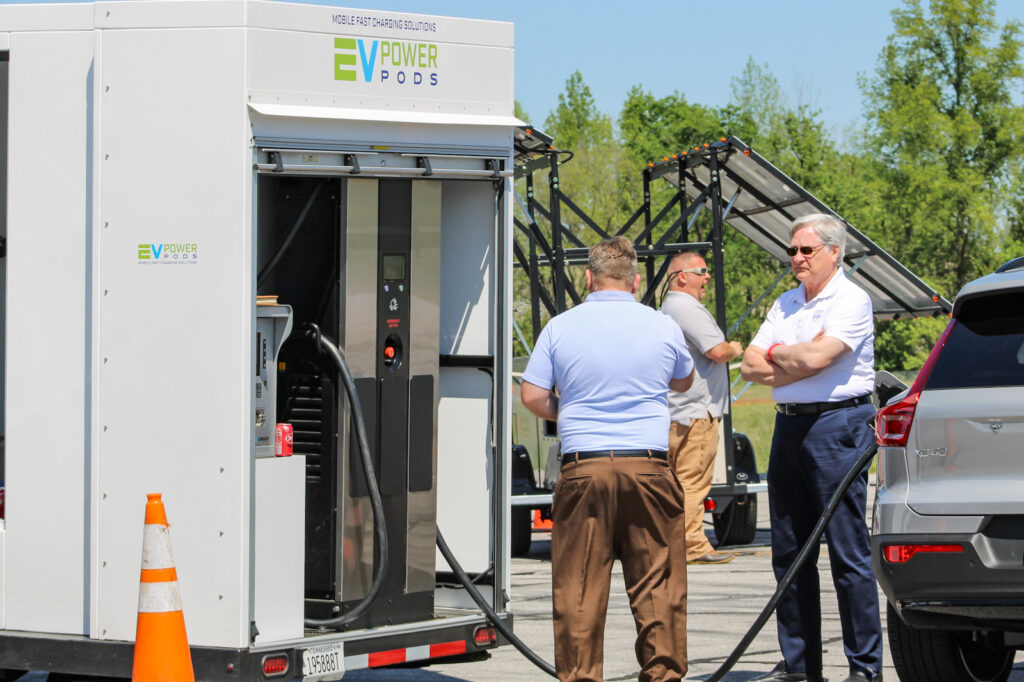
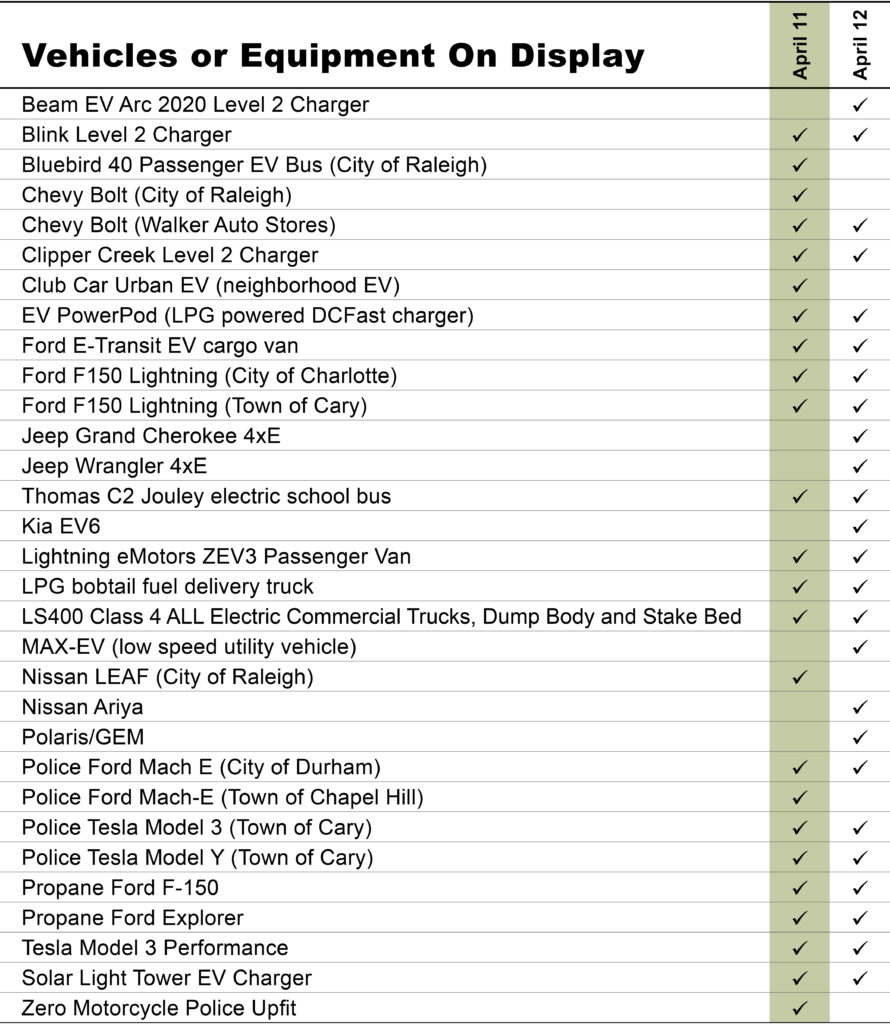
 Clean Transportation Demonstration Days start with classroom instruction before the ride and drive begins. This year, speakers from Alliance Autogas, Potter EV, Cenntro, Cary Cartco, Pioneer eMobility and Electrify EVSE presented on topics such as telematics, safety, idle reduction technologies, vehicle electrification, and other strategies that improve fleet sustainability. Following classroom instruction, attendees explored a diverse display of vehicles and alternative fuel technologies such as electric and alt-fuel vehicles, buses, police vehicles, utility vehicles, charging equipment and more.
Clean Transportation Demonstration Days start with classroom instruction before the ride and drive begins. This year, speakers from Alliance Autogas, Potter EV, Cenntro, Cary Cartco, Pioneer eMobility and Electrify EVSE presented on topics such as telematics, safety, idle reduction technologies, vehicle electrification, and other strategies that improve fleet sustainability. Following classroom instruction, attendees explored a diverse display of vehicles and alternative fuel technologies such as electric and alt-fuel vehicles, buses, police vehicles, utility vehicles, charging equipment and more.
Currently, the clean transportation team is hosting webinars through the Sustainable Fleet Technology Webinar Series, a collaborative partnership with NAFA Fleet Management Association and The 100 Best Fleets, to share the best practices and information on the latest fleet technologies.
2023 SUSTAINABLE FLEET TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE & EXPO
In 2014, the Center held the Southeast Alternative Fuels Conference. In 2017 the conference was renamed the Sustainable Fleet Technology (SFT) Conference & Expo was held to expand education, training, and networking on advanced clean transportation technologies. The event has been hosted every year since (even going virtual for two years during the pandemic).
 Registration for the 2023 Sustainable Fleet Technology Conference & Expo is open now! Join us on August 14-16, 2023 in Raleigh, North Carolina. Come and learn from your peers and experts. Or, join us and share your expertise – opportunities to sponsor, exhibit, and display vehicles are still available.
Registration for the 2023 Sustainable Fleet Technology Conference & Expo is open now! Join us on August 14-16, 2023 in Raleigh, North Carolina. Come and learn from your peers and experts. Or, join us and share your expertise – opportunities to sponsor, exhibit, and display vehicles are still available.
The 2023 SFT Conference will feature keynote presentations, 50+ panelists, breakout sessions in 3 conference tracks, indoor vehicle/equipment display and plenty of networking opportunities to engage with more than 350 other registered attendees. Attendees will be able to attend 4 breakout sessions where they can choose the session that best fits their needs or interests across 3 conference tracks:
A. Funding & Planning
- Federal Funding Sources
- Data for Sustainability and Success
- Innovative Funding
- Training for Success
B. Vehicle Technologies
- New Horizons: AI and Autonomous Vehicles
- Sustainable Trucking Solutions
- Advancements in Engines, Powertrains, and Batteries
- Off-Road Equipment
C. Fueling & Charging Infrastructure
- Longer-Term Planning for Infrastructure Deployment
- Managing Demand Charges
- New Models for Fueling and Charging
- Integrating Facility and Fleet Energy Planning
Learn more and register now at www.sustainablefleetexpo.com.
GRANT FUNDING TO IMPROVE AIR QUALITY & ACCELERATE FLEET SUSTAINABILITY
The Transportation sector represents the largest contributor to North Carolina’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions according to a statewide inventory of GHG emissions produced by the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality’s Division of Air Quality (DAQ). The Transportation sector represents about 36% of all GHG emissions with onroad light-duty gasoline vehicles representing 72% of Transportation sector GHG emissions in 2018, while on road medium/heavy-duty diesel vehicles are the next largest contributor at 16%.
 Emissions from the Transportation sector decreased by an estimated 3% from 2005 to 2018 in North Carolina according to the DAQ. The fact that on road vehicle GHG emissions decreased while vehicle-miles traveled increased over this period demonstrates the effectiveness of vehicle fuel efficiency improvements. The Clean Fuel Advanced Technology (CFAT) supported a diverse set of projects that included truck stop electrification and supporting the use of electric motorcycles for a municipal police patrol as well as propane powered delivery vehicles and electric vehicle charging stations.
Emissions from the Transportation sector decreased by an estimated 3% from 2005 to 2018 in North Carolina according to the DAQ. The fact that on road vehicle GHG emissions decreased while vehicle-miles traveled increased over this period demonstrates the effectiveness of vehicle fuel efficiency improvements. The Clean Fuel Advanced Technology (CFAT) supported a diverse set of projects that included truck stop electrification and supporting the use of electric motorcycles for a municipal police patrol as well as propane powered delivery vehicles and electric vehicle charging stations.
Other types of projects funded by CFAT has included infrastructure projects such as fueling stations and electric vehicle charging stations, purchasing alternative fuel and electric vehicles, diesel and propane retrofits, idle reduction systems, and more. See link HERE for a list of projects supported by the CFAT project.
“The CFAT project aims to promote and accelerate the adoption of new clean transportation technologies,” said Heather Brutz, Director of the Clean Transportation program at NCCETC.
Propelling Public Education on Clean Transportation Technologies

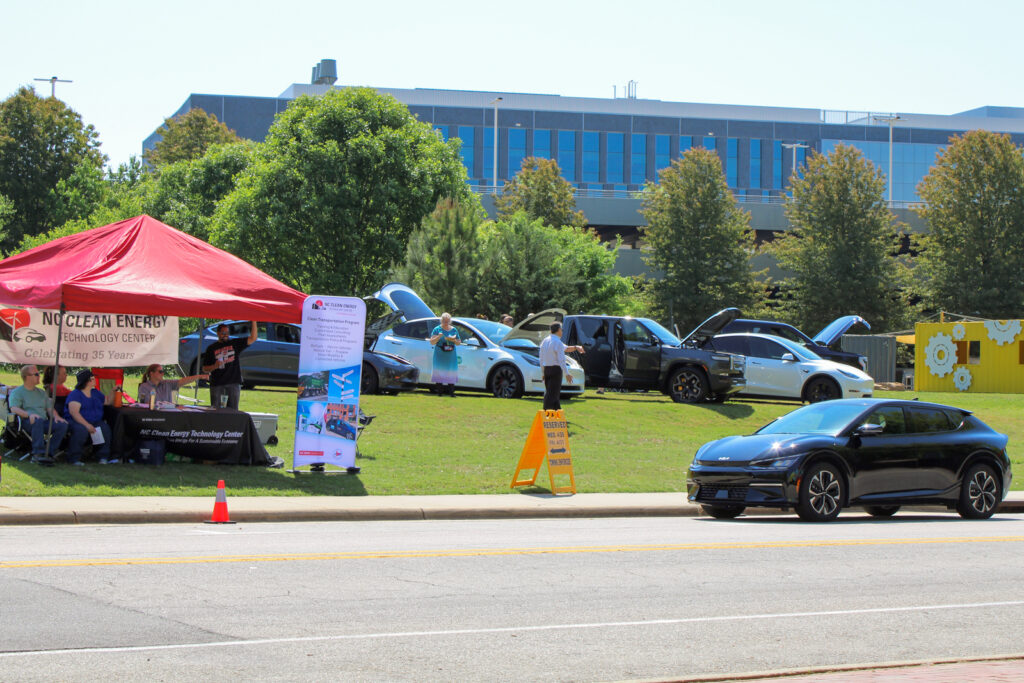
The initial CFAT project started by Tazewell also included education and outreach activities that included billboards, workshops and conferences that continue today with Ride & Drive and Vehicle Displays for a variety of audiences to provide an opportunity for attendees to learn more about clean transportation technologies including electric vehicles (EVs) and other alternative fuel vehicles (AFVs), along with dealers and local EV drivers onsite to answer questions about the driving experience behind the wheel of an EV.
The Student Art Contest is another annual event hosted by the NCCETC. Students from kindergarten, middle and high schools across North Carolina are invited to submit their artwork for a chance to be featured on billboards across the state. Earlier this month, NCCETC announced the 2023 “Keep Our Air Clean” Student Art Contest winners.
Heather Brutz created the Student Art Contest while drawing on her previous experience as a middle school teacher. “The art contest is an engaging way to get young people involved in spreading awareness about the ways we can reduce air pollution from vehicles,” Brutz said. Students were asked to create art focused on actions that people can take to reduce air pollution from vehicles and help keep the air clean. NCCETC congratulated three artists located in Kernersville, Hampstead, and Cary, NC.
SPECIAL PROJECT SUPPORT
At the end of 2020, NCCETC partnered with Roanoke Electric Cooperative to demonstrate cutting edge vehicle-to-grid technology. For two years the Cooperative worked with Fermata Energy to pilot the first electric vehicle charging system that meets the North American standard for two-way current as verified by Underwriters Laboratories (UL). Findings from the demonstration show the positive economic potential for using bidirectional charging technologies to feed energy stored in electric vehicle batteries back to charging sites, especially when the grid is experiencing high demand.
As the market share of EVs continues to grow, there is a nationwide call to establish robust charging infrastructure and electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) to fuel transportation electrification in the U.S. To assist planners and developers in selecting the perfect site to fit their charging needs, NCCETC recently developed a customizable tool for prioritizing the placement of EV chargers. The EVSE Suitability GIS product is not only able to consider several variables relevant to determining charging infrastructure siting benefits, but also has a custom weighting function so developers can tailor the weight of each variable being considered to their unique situation.
NCCETC’s Alexander Yoshizumi coordinated with Roanoke Electric Cooperative while creating the EVSE Suitability GIS tool, identifying factors to include in the suitability tool in addition to the approximate weight that each factor should be given. The GIS product was created using data for the five counties covered by Roanoke Electric Cooperative: Bertie, Gates, Halifax, Hertford, and Northampton.
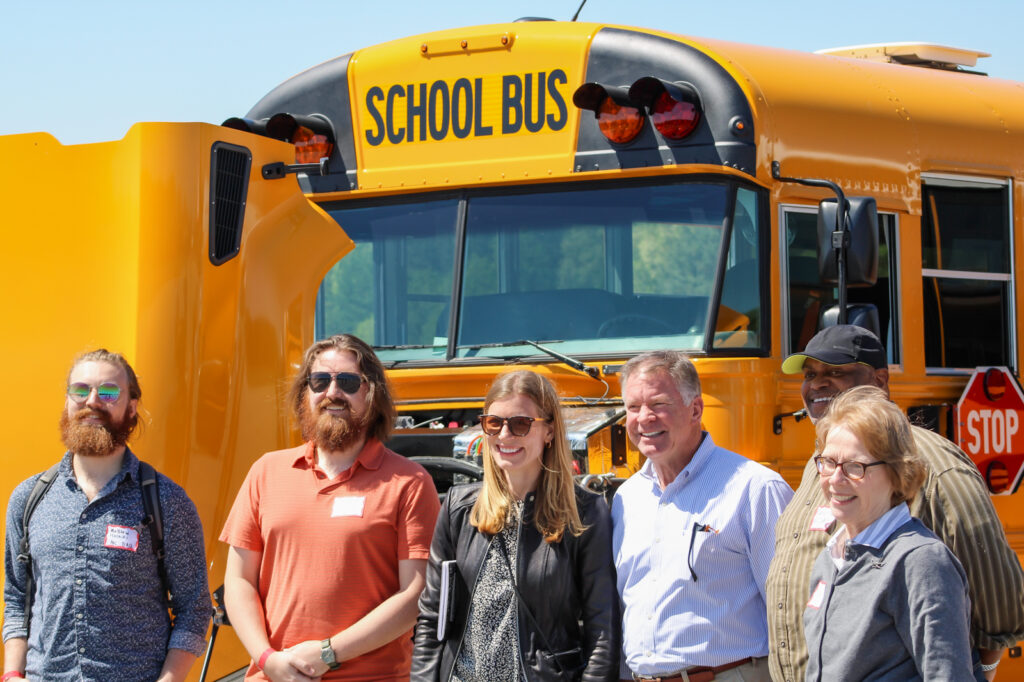
Last year, NCCETC staff provided assistance to the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI) as they applied for grant funding to support cleaner student transportation in North Carolina. Following their groundbreaking award of VW Settlement funds for a new electric school bus in 2021, the EBCI received notice from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for an award for four additional electric school buses in 2022. EBCI will be replacing five diesel school buses with four new electric buses in collaboration with the Cherokee Boys Club (CBC) and the NCCETC. This award marked The Eastern Band as the first tribe east of the Mississippi to be awarded grant funding through the Diesel Emissions Reduction Act (DERA) Program administered by the EPA.
The staff at NCCETC provides technical assistance to fleets interested in building toward a sustainable fleet. The Clean Transportation team has previously assisted municipalities such as the Town of Apex and Morrisville to assess their fleet utilization and ultimately transition to zero-emission vehicles and electrify their fleet.
This article is part of a series highlighting the work done by the NC Clean Energy Technology Center throughout its history in celebration of its 35th Anniversary. View the previous article to learn how the Training program at NCCETC provides educational opportunities for individuals to get the training and credentials they need to launch their clean energy careers and supports professionals seeking to integrate clean energy into their day-to-day work.
 Those who drive EVs have several options when it comes to choosing the electric vehicle service equipment (EVSE) to recharge their batteries. EVSE charging is classified by the power output of the charger, which affects the rate at which the batteries are charged.
Those who drive EVs have several options when it comes to choosing the electric vehicle service equipment (EVSE) to recharge their batteries. EVSE charging is classified by the power output of the charger, which affects the rate at which the batteries are charged.